Elements
and Principles of Design
Introduction to Color
Colors displayed on a computer monitor are called additive colors. They are
created differently than printed or pigment colors. A color management system
attempts to minimize this difference.
Additive Color - (computer monitor, television, theater lighting) direct
light
A computer monitor uses three phosphors that appear as red, green, and blue
when activated. Other colors are made by combining different intensities of
these three colors.
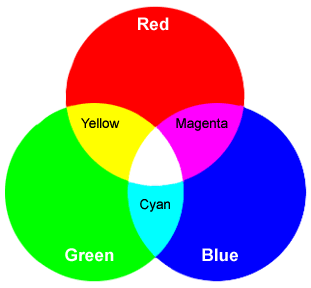
Primary additive colors - red green and blue (RGB) are the primary colors.
They can not be created by any combination of other colors.
Secondary additive colors - The secondary colors are cyan, magenta and yellow.
Printing is based on CMYK color - the secondary colors of cyan, magenta, yellow
and black (K)
Pigment Color - (paint) reflected light
Pigment color is created when a pigment absorb certain light wavelengths and
reflects others. For example, a blue shirt absorbs all wavelengths except blue,
which is reflected. The color wheel based on the three primary colors: red,
yellow and blue, was developed in 1666 by Sir Isaac Newton.
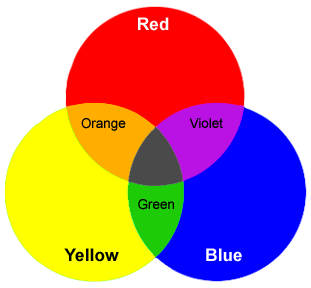
Primary pigment colors - red, yellow and blue are the primary colors. All
other colors are derived from these three hues.
Secondary pigment colors - green, orange and purple are created by mixing
the primary colors.
Tertiary colors - yellow-orange, red-orange, red-purple, blue-purple, blue-green
and yellow-green are the colors created by mixing the secondary colors.
Complementary colors - opposite colors on the color wheel (pigment color
example: red-green) create a sense of excitement or disharmony
Analogous colors - 'neighboring' colors on the color wheel (pigment color
example: red-orange) create a sense of harmony
The Photoshop Color Picker allows you to create color by six means (normally,
you will work in Photoshop in the RGB color mode)
HSB (Hue, Saturation and Brightness) - color can be defined by
its hue (wavelength), saturation (chroma, purity or intensity) and brightness
(value)
Hue - is the color's name (orange, blue, etc.). It is located on the
color wheel - expressed as a degree between 0° and 360°.
Saturation - is the purity of the color. Saturation is the amount of
gray in proportion to the hue - measured from 0% (gray) to 100% (fully saturated).
Brightness - is the relative lightness or darkness of the color -measured
from 0% (black) to 100% (white).
RGB (Red, Green and Blue) - the three primary additive colors
The intensity of each color is measured on a scale from 0 to 255 (8 bits
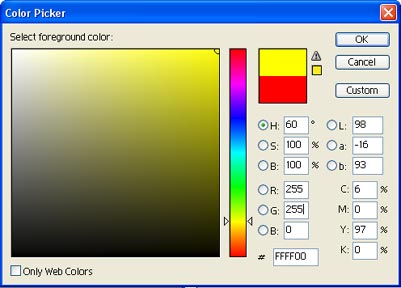
of information). As shown below on the Photoshop Color Picker, yellow is created
by a combination of 255 red, 255 green, and 0 blue.
LAB (Lab mode)
L - the lightness component can range from 0 to 100.
a - is the green-red axis
b - is the blue-yellow axis. Both axis range from +128 to -128.
CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow and Black) - the secondary additive colors
and black are used in printing. They are measured as a percentage.
The intensity of each color is measured on a scale from 0 to 255 (8 bits
of information). As shown below on the Photoshop Color Picker, yellow is created
by a combination of 255 red, 255 green, and 0 blue.
# (Web color) - this six digital number is the hexadecimal equivalent
of the RGB color.
This number is used in HTML code for color. As in the example, #FFFF00 means
255 red (the first two numbers), 255 green (the next two) and 0 blue (the
last two numbers). F represents the hexadecimal number 15.
Custom - allows to you work with matching color systems such as Pantone
Color theory links
Adobe
-color theory
Color Wheel
Pro -color theory
introduction | components
| elements of design | principles
of design | color | indicators of depth


