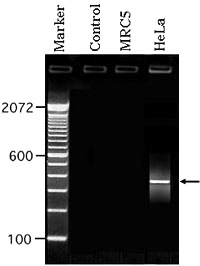

It is now known that 80-90% of cervical carcinomas (cancers) contain HPV16 or HPV18 DNA.
The relationship between HPV infection (which is common) and malignant cell transformation (which is rare) is complex and still poorly understood. However, cervical cancer is one of the most common cancers, accounting for 6% of all malignancies in women.
Epidemiologic studies have demonstrated that the major risk factor for development of cervical carcinoma is HPV infection, which far outweighs other known risk factors.